증류공정은 plant operation에 있어서 핵심적인 공정이며 아울러 많은 에너지를 소비하는 시스템이므로 grassroot design을 하거나 revamping을 할 경우 에너지 소비 즉 운전비용을 줄일 수 있도록 고민을 해야 한다. 이를 위해 여러 운전 조건이 허용한다면 아래 언급된 vapor recompressor를 이용할 경우 경제성이 있을 것으로 판단이 된다.
에너지 소비를 줄이기 위해 쉽게 고려할 수 있는 방법이 운전변수 조정이나 preheating 등 폐열회수 방법 혹은 pinch technology를 이용한 heat integration이 있지만, 보다 효과적인 방법으로 heat pumping을 고려할 수 있다.
heat pump를 이용하는 방법중 하나는 overhead vapor를 직접 압축하는 방법으로 overhead vapor를 압축하여 과열된 vapor를 reboiler로 보내어 bottoms을 가열한 후 이 vapor는 응축후 reflux하거나 product로 run down한다. 또 다른 방법으로 external vapor를 압축하는 방법으로 buffer fluid를 이용하여 condenser에서 이 액체 buffer fluid가 증발하면서 overhead vapor를 응축시키고, 증발된 buffer fluid는 compressor에서 압축하여 reboiler로 보내져서 이 곳에서 다시 응축하여 closed loop를 완성한다. 이는 직접 vapor를 압축할 경우 매우 hazardous하거나 corrosive할 경우 대안으로 이용할 수 있다.
마지막으로 bottom flashing방법이 있으며, 이는 reboiler가 필요없고 bottoms를 let down하여 더 낮은 온도, 압력에서 증발이 일어난다. heat source는 overhead vapor가 되어 condenser에서 이러한 bottoms 액체와 열교환이 된 후 액체가 증발된 vapor는 compressor로 들어가서 압축된 후 다시 column bottom으로 들어간다.

Vapor를 압축한 증류공정의 최적화
화학공정에서 증류탑을 이용한 분리공정은 품질에 직접 영향을 줄 수 있는 매우 중요한 설비이며 아울러 에너지를 많이 소비하는 공정이다. 따라서 투자비는 증가하지만 에너지 소비를 줄여 운전비를 낮출 수 있는 heat integration, heat pumps, thermal coupling 등의 방법들이 적용되고 있다.
증류공정의 overhead vapor 에너지를 이용하되 여기에 외부의 기계적 에너지를 가미하여 증류탑 bottom의 reboiling에 활용할 수 있다. 이는 column overhead vapor의 잠열을 이용하되 driving force 및 운전온도를 높여 column bottoms에 열전달이 가능하도록 구성하는 것이다. PP splitter에서 typical하게 적용하여 에너지 소비 절감이 가능하며 운전의 신뢰성도 확보할 수 있다.
conventional distillation에는 top에 condenser, 그리고 bottom에 reboiler가 배치되지만 heat pump compressor system을 적용할 경우 condenser와 reboiler를 combining할 수 있다.

conventional system
온도가 낮은 overhead vapor를 온도가 높은 bottoms에 열흐름을 제공하기 위해 외부의 에너지가 필요하며, 이 역할을 HPC (Heat Pump Coompressor)가 수행하여 hydraulic 및 thermal flow 목적으로 온도와 압력을 높이기 위해 vapor를 압축한다.

combined HPC system
reboiler에 필요한 열량을 제공한 이후 이 overhead vapor는 응축이 되어 일부는 다시 reflux로 돌려 보내고 일부는 제품으로 run down할 수 있다.

This schematic depicts a conventional (left) and a vapor-recompression (right) type of distillation column for a typical C3 splitter column
HPC system에서 응축된 overhead vapor는 flash tank로 보내어 이 곳에서 상분리가 된 후 liquid만 reflux로 보내고 flash된 vapor는 다시 HPC로 도입된다.
alter case로서 overhead vapor 대신 reboiler outlet vapor를 압축한다. 이를 위해 reboiler outlet의 압력을 let down하여 flashing 및 포화온도를 낮추어 overhead vapor보다 운전온도를 낮추는 것이 핵심이다. 이후 증발된 bottoms는 compressor를 이용하여 column으로 return시킨다. 이 경우 column reboiling과 condensing duty가 match되지 않을 경우를 대비해 auxiliary condenser나 auxiliary reboiler가 필요할 수 있다.
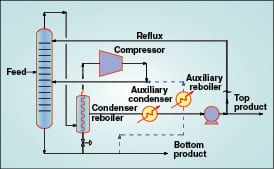
An alternate configuration for vapor recompression distillation consists of compressing the reboiler outlet vapors instead of column overhead vapors
conventional distillation의 경우 운전압력은 heating media나 cooling media의 온도에 제한을 받아 상대휘발도를 이용하기 위해 더 낮은 압력에서 운전하는데 한계가 있다. 하지만 HPC의 경우 column 압력을 낮추어도 compressor에서 가압하여 reboiler heat source역할을 할 수 있어서 운전의 flexibility를 높일 수 있다.
이러한 HPC system은 top과 bottom의 온도차이가 낮은 (close boiling) 경우에 적용할 수 있다. 다만 top과 bottom의 온도 차이가 클 경우 외부 power가 커져야 하며 이는 경제성이 떨어지게 된다. (전기 비용이 steam이나 CW와 같은 utility 비용보다 큼)
이를 통해 비교적 적은 외부 에너지를 이용하여 codenser와 reboiler사이에서 많은 양의 heat을 이동시킬 수 있어서 에너지 절감이 가능하다. 아울러 heating source, cooling source의 온도에 무관하게 증류 performance를 위해 얼마든지 운전압력 조정이 가능하다. close boiling system의 경우 압력이 낮을수록 상대휘발도가 개선이 되어 분리가 잘 됨에 따라 column height와 reflux양을 줄일 수 있다.
PP spliter design case study
SRK를 이용하여 steady state rigorous simulation을 통해 두 system을 비교한 결과는 아래와 같다. 먼저 shortcut distillation model로부터 initial estimate인 최소이론단수 (Fenske method)와 최소 reflux양 (Underwood method)을 산출한다.
1. conventional column system
분리목적상 열역학적으로 가능한 낮은 압력이 바람직한데, CWS/CWR 조건이 32/38도임에 따라 condenser design을 위한 approach temperature 10도를 감안하여 overhead vapor의 dew point는 42도이고, 여기에 equivalent pressure가 17K/G이므로 운전은 이 압력 이하에서는 어렵게 된다.
shortcut module을 통해 평균 상대휘발도를 이용하여, underwood method에 따른 최소 환류량은 10.51로 계산된다. 이후 rigorous model을 이용하여 최소환류량의 1.5~1.6배를 적용하여 최적의 환류량으로 고려한다.
이론단수는 120~240로 다양하며 이는 reboiler duty에 따라 가변적이다. reboiler duty는 곧 reflux ratio와 비례관계이다. 아래 table상 이론단수 180을 넘어서면 reboiler duty가 크게 줄지 않아 이후 이론단수를 늘려도 reboiler duty를 줄이는데 경제성이 떨어지게 되어 180단으로 fixed한다.

This plot shows that there is no significant reduction in the reboiler duty beyond 180 trays
아래 curve와 같이 reboiler와 condenser duty가 최소가 되는 feed tray 위치를 선정한다. 최종적으로 max flooding 75%를 기준으로 column 직경은 6250mm이다.

The simulation model for the conventional distillation system indicates that the optimum duty is achieved when the feed tray is located at tray 142
2. HPC column system
일반적으로 column module내 condenser와 reboiler가 포함된 built-in algorithm을 이용하므로 별도로 reflux나 reboiler recirculation stream을 define할 필요가 없다. 하지만 HPC system에서는 reboiler와 condenser가 integration되어 compressor설계에 영향을 주는 가장 큰 변수가 reboiler temperature approach이다. 즉, reboiler outlet과 heat source인 compressed overhead vapor inlet온도 차이이다.
이러한 configuration을 modelling하기 위해 reboiler와 condenser가 없는 column module을 적용하고 여기에 열교환기를 추가한다. 즉, column overhead vapor와 bottom stream을 연결하며 이는 더 이상 column built-in algorithm이 아니다.
여기에 external recycle loop에 compressor를 추가하고 수렴을 용이하게 하도록 간접 modeling방법을 이용한다. 즉, 아래와 같이 top tray를 나가는 stream에 대해 pseudostream을 만들어 물성치와 유량을 generation하여 recycle loop의 input으로 이용한다. 이에 대한 이점으로는 recycle stream의 convergence model을 once through 계산으로 대체하여 수렴이 쉽게 된다.

An indirect modeling method using a psuedostream was used to simulate vapor-recompression-assisted distillation
HPC의 가장 큰 장점은 앞서 언급한 것처럼 더 이상 CW를 사용하지 않음에 따라 column압력을 더 낮출 수가 있다. 이후 compressor를 이용하여 reboiler feed stream (bottoms) 온도보다 충분히 높은 상태에서 응축이 되도록 overhead vapor를 가압한다.
위 온도차이가 낮을수록 즉, compressed overhead vapor온도가 낮을수록 reboiler size는 커지지만 압축비를 줄일 수 있어서 compressor 투자비와 운전비를 줄일 수 있다. 설계를 위해 열교환기 approach temperature를 20도로 고려하여 compressor 후단온도가 70도가 되도록 후단압력을 설정한다. 아울러 최적의 압축비를 감안하여 suction pressure인 column 운전압력을 설정하여 이 경우 12K/G로 결정한다.
column 운전압력을 더 낮출 경우 compressor suction압력이 낮아져서 압축 단수가 늘어야 하며 결국 투자비가 증가할 수 있다. reboiler heat duty를 맞추고 외부의 disturbance에 대해 column system의 heat balance를 유지하기 위해 압축된 vapor의 대부분은 reboiler로 보내지고 나머지는 control용으로 auxiliary condenser로 보내거나 feed preheating용 economizer로 보내질 수 있다. 위 운전압력에서 shortcut method를 이용하여 최소환류량을 산출하고 여기에 1.5~1.6배를 적용하여 이론단수를 구한다.
3. Result
max jet flooding은 동일하게 75%를 적용하여 column diameter를 계산하였고 비교를 위해 simulation시에 이론단수를 고려하였다. compressor power는 polytropic efficiency 75%를 적용하였다. 결과적으로 요약하면, HPC를 적용할 경우 column diameter와 height를 줄여 하나의 column으로도 가능할 수 있으며, auxiliary condenser의 duty는 작기 때문에 열교환기 크기를 줄일 수 있고 reflux pump 크기도 줄일 수 있으며, conventional model에서의 liquid transfer pump도 필요가 없지만 compressor는 필요하다. market 상황에 의존하게 되므로 정확한 경제성 분석은 어렵지만 HPC system을 적용하므로서 운전비를 낮출 수 있다.
conventional system의 경우 steam, CW, reflux pump의 power 등이 주요 운전비용이며 product pump의 운전비는 두 case 모두 동일하므로 운전비 비교에서 제외하였다. HPC system의 경우 auxiliary condenser를 위한 CW, reflux pump와 compressor의 power가 주요 운전비용이다. 결과적으로 후자의 경우 운전비가 적게 들어 년 7백만달러의 절감효과가 있다. 아울러 auxiliary condenser 대신 feed를 heating하기 위한 process-process열교환을 할 경우 CW는 더 줄일 수 있다.
기존 공장에 HPC를 적용하기 위해 먼저 기술적으로 가능한지 검토하고 (즉, hydraulically, thermally proven) 이후 전기료와 스팀비용을 고려하여 경제성 분석을 한다. rule of thumb로서 top과 bottom온도 차이가 25도 이하일 경우 HPC를 적용할 수 있다. 즉, 온도차이가 클 경우 bottom을 가열하기 위해서는 overhead vapor온도가 더 높아야 하며 그만큼 더 압축을 해야 하므로 운전비용이 매우 커지게 된다. 여기에 추가적인 rule of thumb으로 compressed overhead vapor온도가 bottoms온도보다 30도 이상이 되어야 전열면적을 줄여 투자비를 낮출 수 있다.
#vapor_recompressor#HPC#heat_pump#buffer#bottom_flashing#conventional_distillation#상대휘발도#shortcut#underwood#fenske#jet_flooding#polytropic#ROI
'공정설계' 카테고리의 다른 글
| POE (Polyolefin) Elastomer (0) | 2025.01.03 |
|---|---|
| 초저온 공장의 Dryout을 위한 고려사항 (1) | 2024.12.27 |
| DMF process 이해 (0) | 2024.12.27 |
| EO / EG 공정 이해 (2) | 2024.12.26 |
| Solid H2 storage 이해 (1) | 2024.12.25 |