LOPA란 Layer of Protection Analysis의 약어로서 IPL (Independent Protection Layer) 기준을 만족하는 safeguard를 identify할 수 있는 semi-quantitative methodology라고 할 수 있다. (위험성을 분석하고 평가하기 위한 간단한 정량적 도구)
위험성 평가를 할 때 시나리오로서 여러 개의 cause-consequence가 존재하더라도 하나의 cause-consequence pair에 국한하여 평가한 후 다른 pair에 대해 평가를 수행한다.
1990년대 develop된 LOPA는 위험성평가의 tool로서 이용되기 시작하면서, CCPS (Center for Chemical Process Safety)에서 2001년 Layer of Protection Analysis: Simplified Process Risk Assessment (CCPS, LOPA)라는 concept book을 발간하였다.

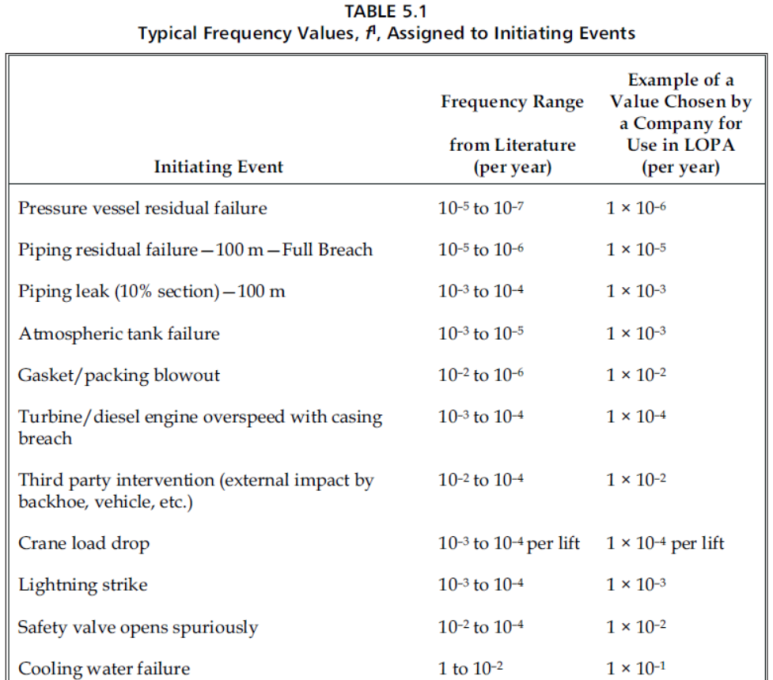
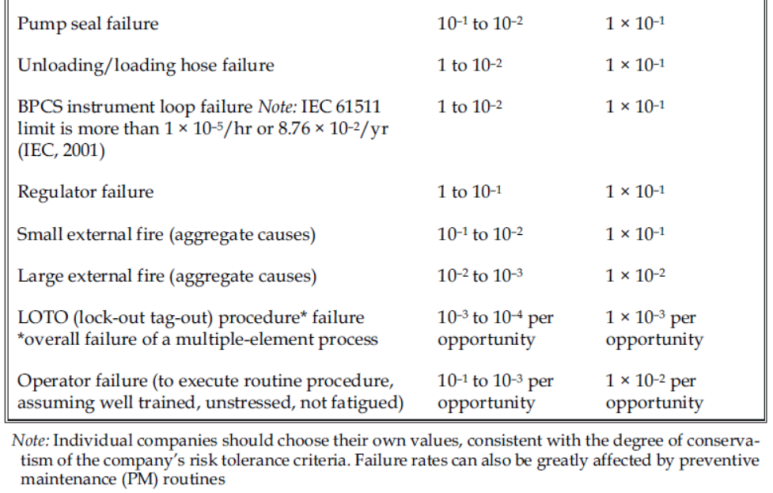
CCPS에서는 IE (Initiating Event)와 IPL (Independent Protection Layer)에 대한 기준 및 IE probability와 IPL의 PFD (Probability of Failure on Demand) 값을 제시하고 있다.
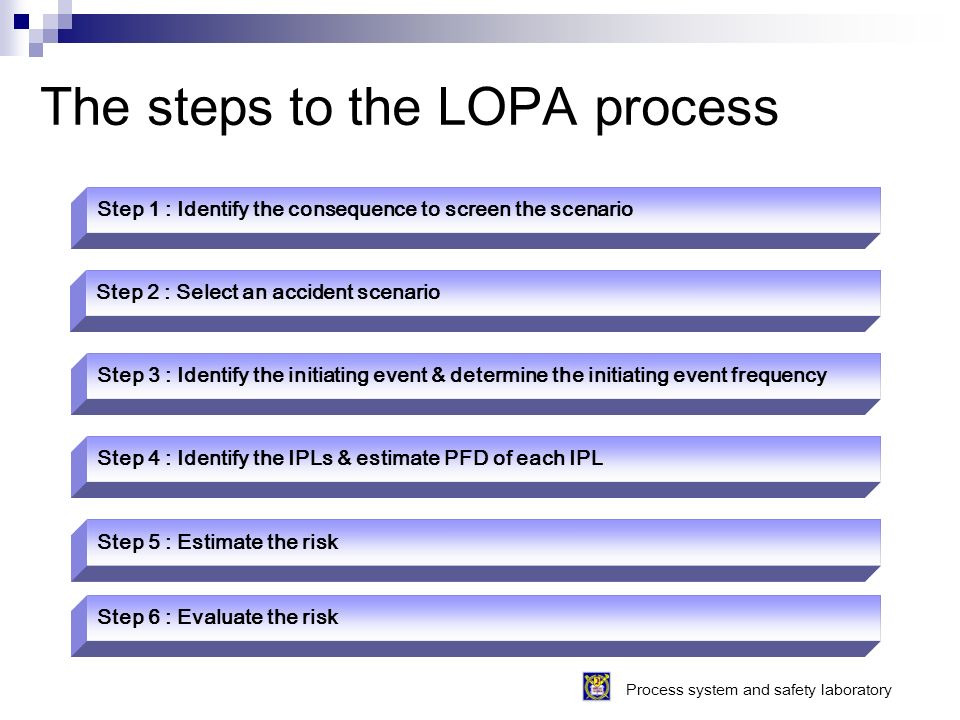
기본적인 LOPA step은 아래와 같다.
먼저 시나리오를 screen하기 위해 consequence를 identify한다.
accident scenario을 선택한다.
IE를 identify하고 IE frequency를 결정한다.
IPL을 identify하고 IPL의 PFD를 estimation한다.
IE frequency와 IPL PFD를 조합하여 consequence에 대한 unmitigated frequency를 결정한다.
risk를 평가하여 TMEL (Target Mitigated Event Likelihood)보다 확률이 높다면 추가적인 IPL을 고려한다.
INITIATING EVENTS (IE) Frequency
기본적으로 incident에 대한 failure나 error의 combination은 아래와 같다.
Above ground piping: leak (pipe size ≤ 150 mm, 6 in)
Aboveground piping in typical service: full breach failure (pipe size > 150 mm, 6 in)
Aboveground piping: full breach failure (pipe size ≤ 150 mm, 6 in)
Aboveground piping: leak (pipe size >150 mm, 6 in)
Atmospheric tank: catastrophic failure
Atmospheric tank: continuous 10 mm diameter leak
BPCS control loop failure
Complete primary pump seal failure
Failure of double check valves in series
Fire-resistant insulation and cladding on vessel
Hose failure, leak and rupture
Human error during a routine task that is performed >=once per week
Human error during a task that is performed < once per month
Human error during a task that is performed between once per month and once per week
Localized loss of power - Single circuit loss of power
Premature opening of spring-loaded relief valve
Pressure regulator failure
Pressure vessel: catastrophic failure
Pump seal leak
Pump, compressor, fan, or blower failure
Screw conveyor failure
Screw conveyor overheating of materials
Single check valve failure
Single circuit loss of power
Spurious operation of SCAI
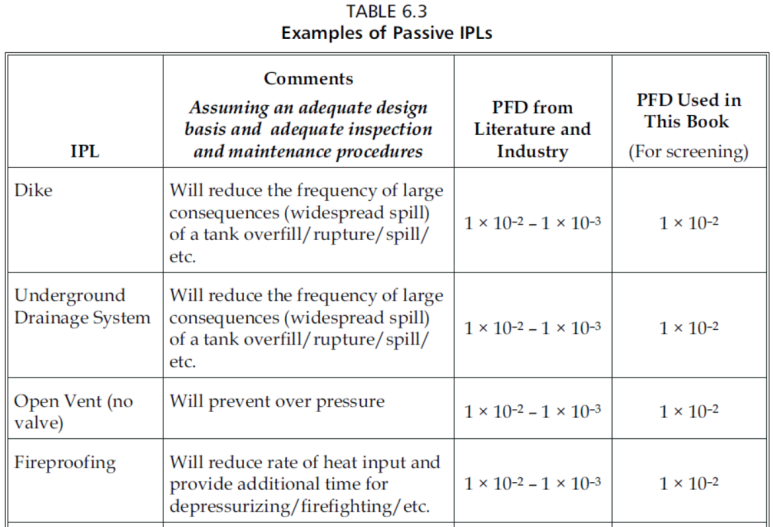
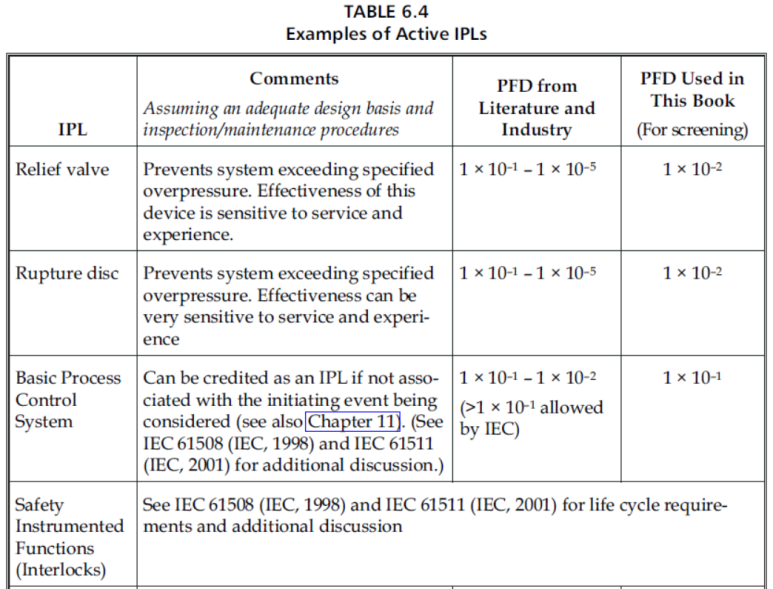
INDEPENDENT PROTECTION LAYER
IPL은 시나리오가 원치 않은 결과로 진행되지 않도록 하기 위한 device, system 혹은 action으로서 IE 혹은 시나리오와 관련된 다른 protection layer와 독립적이어야 한다.
- Adjustable Movement-Limiting Device
- Automatic Explosion Suppression System for Process Equipment
- Automatic Fire Suppression System (within process equipment)
- Automatic Fire Suppression System for a Room
- Automatic Fire Suppression System for Local Application
- Buckling Pin Isolation Valve (BPIV)
- Buckling Pin Relief Valve
- Captive Key/Lock System
- Check Valve
- Conservation Vacuum and/or Pressure Relief Vent
- Continuous Pilot
- Continuous Ventilation with Automated Performance Monitoring
- Continuous Ventilation without Automated Performance Monitoring
- Dikes, Berms, and Bunds
- Drainage to Dikes, Berms, and Bunds with Remote Impoundment
- Dual Spring-Operated Pressure Relief Valves
- Emergency Ventilation Initiated by Safety Controls, Alarms, and Interlocks (SCAI)
- End-of-Line Deflagration Arrestor
- Excess Flow Valve
- Explosion Isolation Valve
- Explosion Panels on Process Equipment
- Fire-Resistant Insulation and Cladding on Vessel
- Frangible Roof on Flat-Bottom Tank
- Gas Balance/Adjustable Set Pressure Surge Relief Valve
- Human Response to an Abnormal Condition
- Human Response to an Abnormal Condition with Multiple Indicators…
- In-Line Deflagration Arrestor
- In-Line Stable Detonation Arrester
- In-Line Unstable Detonation Arrester
- Line Containing a Fluid with the Potential to Freeze
- Mechanical Overspeed Trip on a Turbine
- Mechanically Activated Emergency Shutdown/Isolation Device
- Multiple Mechanical Pump Seal System with Seal Failure Detection and Response
- Overflow Line Containing a Passive Fluid or with a Rupture Disk
- Overflow Line with no Impediment to Flow
- Permanent Mechanical Stop that Limits Travel
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Pilot-Operated Pressure Relief Valve
- Pipeline Surge Dampening Vessel
- Pressure Reducing Regulator
- Restrictive Flow Orifice
- Rupture Disk
- Safety Control Loop
- Safety Interlock
- SIS Loop
- Spring-Operated Pressure Relief Valve
- Spring-Operated Pressure Relief Valve with Rupture Disk
- Vacuum Breaker
- Vent Panels on Enclosures
모든 IPL이 safeguard이지만, 모든 safeguard가 IPL은 아니다.





CONDITIONAL MODIFIER
추가적으로 risk를 완화시킬 수 있는 조건에 대한 factor를 고려할 수 있다.
- Probability of a hazardous atmosphere
- Probability of ignition inside process equipment
- Probability of ignition outside process equipment
- Probability of uncontrolled reaction initiation
- Probability of Dust explosion
- Probability of vessel rupture explosion
- Probability of vapor cloud explosion
- Probability of deflagration to detonation transition
- Probability of personnel presence
- Probability of injury or fatality
- Probability of equipment damage or other financial impact
- Double jeopardy
- Revealed vs un-revealed failures
- Quantifying double jeopardy
- When the consideration of the Simultaneous failures is valid


ENABLING CONDITIONS
IE가 consequence로 이어지기 위해 동시에 존재하기 위한 조건으로서 예를 들어 IE가 cooling loss이며, 이 경우 batch 반응기에서 발열 폭주 반응으로 과압을 야기한다. 하지만 이는 냉각손실에 민감한 반응시에만 관련이 됨에 따라 회분식 반응기간이 enabling condition이다.

#LOPA#layer#protection#IPL#safeguard#quantitative#methodology#CCPS#PFD#IE
'공정위험성평가 컨설팅' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SIF (Safety Instrumented Function) 이해 (0) | 2025.01.06 |
|---|---|
| 화학 설비의 부식 관련 위험성 평가 사례 (0) | 2024.12.25 |
| PSM 이행상태 평가 관련 방법 및 기준 (2) | 2024.12.22 |
| PSM 자체 감사 (1) | 2024.12.22 |
| 정량적 위험성 평가 (QRA: Quantitative Risk Assessment) (0) | 2024.12.20 |